Using G02 and G03 g-codes with PlanetCNC TNG software
Another two g-codes used to specify machine movements are G02 and G03. They move the machine in an arc, in contrast to G00 and G01 which move the machine in a straight line.
G02 moves the machine in a clockwise arc and G03 moves the machine in a counterclockwise arc.
To use these codes we need to specify the coordinates to which the machine will travel, the offsets to the center of the arc or the arc radius and optionally the number of additional turns the machine will make while performing the move. The speed of these movements is also defined by the F-word (feed rate).
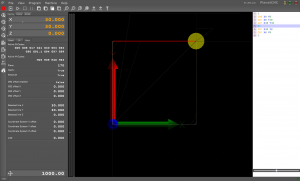
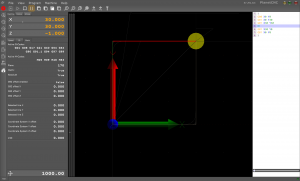
For example: Starting from X0 Y0 Z0, we would like to round a 90 degree corner using a counterclockwise arc to X50 Y50 Z0. To do this we will use the command G03 X50 Y50. But this command isn’t complete yet and the program would signal an error if we tried to use it like that. We still need to specify the center of the arc. This is done by specifying offsets from the starting position or with the deprecated method of specifying the radius.
The offsets are simply the distance from the starting position to the center of the arc. The offsets are separated into components for each axis. The center also needs to be equidistant from both the starting and the destination point. Otherwise the arc won’t be part of a circle and the controller will signal an error accordingly.
As we said, the offsets are the distance the machine would need to move along each axis separately to get to the center. In our case (starting from the origin) this would be 50 units along the Y axis. This also means that the radius of the circle will be 50 units (the radius equals the distance from the center to the origin or destination). Now we need to specify the offsets to the machine. To do this we use I, J and K-words for the X, Y and Z axes accordingly. When we put all this together we get the final code that looks like this: G03 X50 Y50 J50.